Term Page
Post-Conviction Relief How a Private/Nonprofit Partnership Can Help Immigrants Obtain Post-Conviction Relief
Crimes
Post-Conviction Relief
Removal Defense
This webinar will highlight an innovative pro bono model that ensures every immigrant has their full due process rights protected and no person is deported on the basis of an unconstitutional conviction. Led by Rose Cahn from the Immigrant Legal...

In 2016, California enacted California Penal Code § 1473.7, a post-conviction relief vehicle allowing people no longer in criminal custody to vacate legally defective convictions. Ever since, the ILRC has supported advocates to implement this law, including helping to defend the vacaturs from DHS attempts to erode its impact. In Arias v. Garland, a case currently pending before the Ninth Circuit, the court will decide whether 1473.7 should be given full effect, erasing the conviction for immigration purposes. The ILRC helped coordinate Mr. Arias’s amicus strategy and we offer his redacted merits brief as well as the extraordinary amicus briefs submitted in support so that they might help practitioners facing similar arguments. The briefing in the Arias case represents some of the most robust arguments for why 1473.7 vacaturs should be recognized, but we also include below the various prior briefs, advisories, and sample materials we have developed in the defense of the full reach of 1473.7.

Thousands of noncitizens in California are at risk of removal or cannot qualify for immigration relief because they have unlawfully imposed criminal convictions. The good news is that there are several options under California law to eliminate these convictions for immigration purposes, using post-conviction relief (PCR). This Advisory can help advocates to identify which of these forms of California PCR may help your client, and direct you to more resources about how to obtain it.

This advisory provides detailed instruction on how and where to file a motion to reopen for attorneys who have successfully vacated a conviction for immigration purposes and their client is now eligible for termination or a form of relief. In addition, the advisory addresses the impact of the post-departure bar and reinstatement of prior removal order on post-conviction relief motions to reopen.
So, you’re organizing a local town hall or candidate forum about DA and immigration; great! ILRC has developed a number of resources that can be helpful.

The ILRC and partner organizations submitted the attached letter and BIA case summary to OPLA leadership, clarifying that vacaturs issued pursuant to California Penal Code § 1473.7(a)(1) correct legally and procedurally defective convictions, meeting the standard set forth in Matter of Pickering, 23 I&N Dec. 621 (BIA 2003).
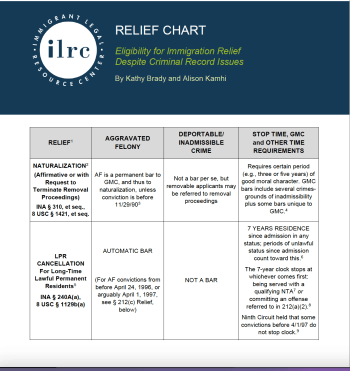
This Chart summarizes the criminal record bars to many forms of relief, to provide a quick way to check whether your client is potentially eligible for relief. See also ILRC, Immigration Relief Toolkit (2018).

With a few exceptions, immigration authorities must use the “categorical approach” to determine whether a criminal conviction triggers a ground of removal. Expert use of the categorical approach may be the most important defense strategy available to immigrants charged with or convicted of crimes. This Update of our long-running article includes discussion of Pereida v. Wilkinson, 141 S.Ct. 754 (2021).

On January 1, 2021, multiple California criminal reform laws took effect. These laws were passed to help all defendants regardless of immigration status, but they can be of special help to noncitizens. Advocates should understand how these laws may help a client’s immigration case. They include:

Immigration law has its own definition of what constitutes a criminal conviction. The Board of Immigration Appeals (BIA) and other courts have held that certain types of pretrial diversion and intervention agreements that result in dismissal under state law can still constitute a conviction for immigration purposes. Practitioners must pay close attention to the structure of such agreements, and the variety of available diversion programs, when evaluating a client’s criminal history and advising about the potential immigration consequences of criminal offenses and dispositions. This advisory discusses when such diversion agreements and programs will constitute a conviction for immigration purposes, strategies to avoid triggering an immigration conviction, and tips for advocating for “immigration-safe” agreements.